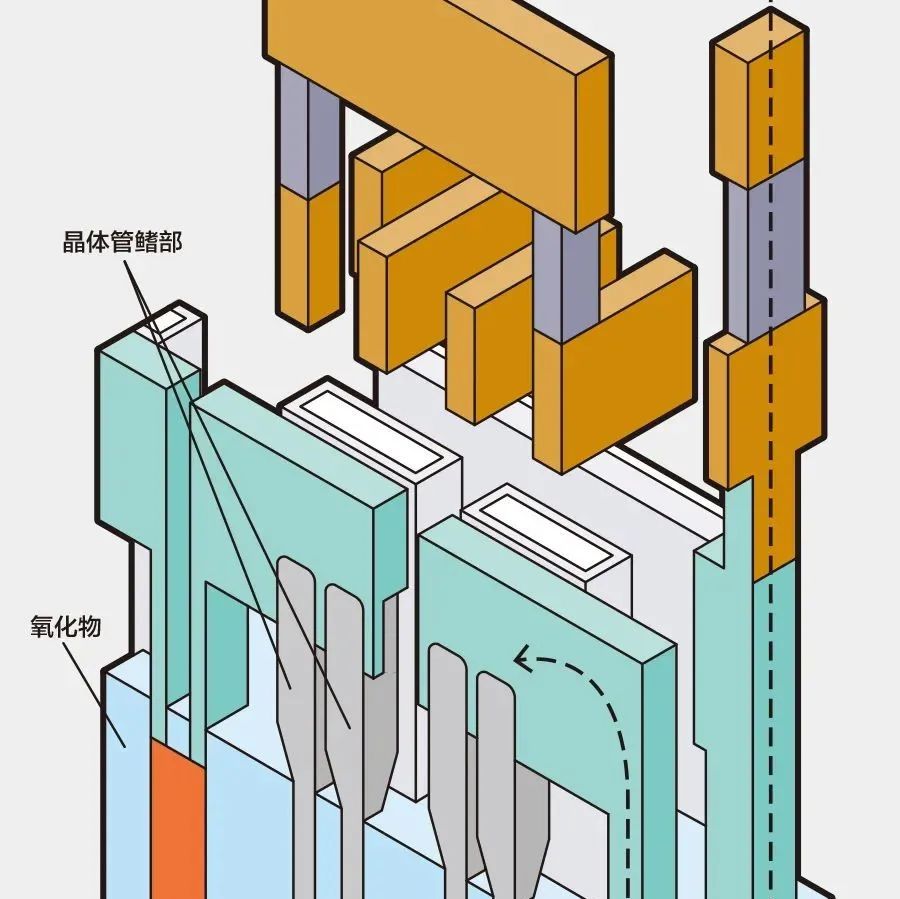
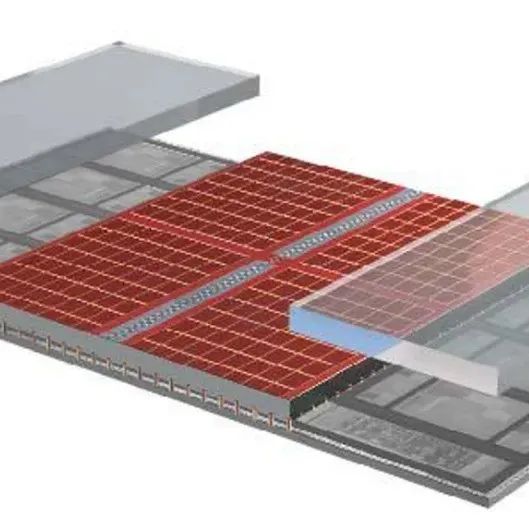
一文了解存算一体芯片
来源:来自 「智前沿」, 作者:王绍迪,谢谢 。









参考文献
[1] L. Lin, X. Liao, H. Jin, and P. Li, “Computation Offloading Toward Edge Computing,” Proceedings of the IEEE (Early Access), Jul. 2019.
[2] C. L. Chen, and C. Zhang, “Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: a survey on Big Data,” Information Sciences, vol. 275, pp. 314-347, Aug. 2014.
[3] W. Wulf, and S. McKee, “Hitting the Memory Wall: Implications of the Obvious,” ACM Computer Architechture News, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 20-24, Dec. 1994.
[4] M. Zidan, J. Strachan, and W. Lu, “The Future of Electronics Based on Memristive Systems,” Nature Electronics, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 22-29, Jan. 2018.
[5] R. Alshahrani, “The Path to Exascale Computing,” in ACM/IEEE ICPDPTA., pp. 123-126, 2015.
[6] R. Nair, S. Antao, C. Bertolli, et al., “Active Memory Cube: A Processing-in-Memory Architecture for Exascale Systems,” IBM Journal of Research and Development, vol. 59, no. 2, pp. 17:1-17:14, Apr. 2015.
[7] W. Kautz, “Cellular Logic-in-Memory Arrays,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. C-18, no. 8, pp. 719-727, Aug. 1969.
[8] H. Stone, “A Logic-in-Memory Computer,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. C-19, no. 1, pp. 73-78, Jan. 1970.
[9] D. Patterson, T. Anderson, N. Cardwell, R. Fromm, K. Keeton, R. Thomas, and K. Yelick, “A Case for Intelligent RAM,” IEEE Micro, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 34-44, Apr. 1997.
[10] S. Li, D. Niu, K. T. Malladi, B. Brennan, and Y. Xie, “DRISA: A DRAM-based Reconfigurable In-Situ Accelerator,” in IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), pp. 288-301, Apr. 2017.
[11] V. Seshadri, D. Lee, T. Mullins, H. Hassan, A. Boroumand, J. Kim, M. A. Kozuch, O. Mutlu, P. Gibbons, and T. Mowry, “Ambit: In-Memory Accelerator for Bulk Bitwise Operations Using Commodity DRAM Technology,” in IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), pp. 273-287, Oct. 2017.
[12] S. R. Agrawal, S. Idicula, A. Raghavan, E. Vlachos, V. Varadarajan, and E. Sedlar, “A Many-Core Architecture for In-Memory Data Processing,” in IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), pp. 245-258, Oct. 2017.
[13] X. Guo, F. Bayat, M. Bavandpour, M. Klachko, M. Mahmoodi, M. Prezioso, K. Likharev, and D. Strukov, “Fast, Energy-Efficient, Robust, and Reproducible Mixed-Signal Neuromorphic Classifier Based on Embedded NOR Flash Memory Technology,” in IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), pp. 6.5.1-6.5.4, Dec. 2017.
[14] H. Wong, and S. Salahuddin, “Memory Leads the Way to Better Computing,” Nature Nanotechnology, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 191-194, Mar. 2015.
[15] L. Wang et al., “Voltage-Controlled Magnetic Tunnel Junctions for Processing-In-Memory Implementation,” IEEE Electron Device Letters, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 440-443, March 2018.
[16] W. Kang, Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, J. O. Klein, C. Chappert, D. R. Ravolosona, G. Wang, Y. Zhang, and W. Zhao, “Spintronics, Emerging Ultra-Low Power Circuits and Systems Beyond MOS Technology,” ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems (JETC), vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 1-42, Sep. 2015.
[17] A. Chen, “A Review of Emerging Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) Technologies and Applications,” Solid-State Electronics, vol. 125, pp. 25-38, Nov. 2016.
[18] J. Borghetti, G. Snider, P. Kuekes, J. Yang, D. Stewart, and R. Williams, “Memristive Switches Enable Stateful Logic Operations via Material Implication,” Nature, vol. 464, no. 7290, pp. 873-876, Apr. 2010.
[19] P. Chi, S. Li, C. Xu, T. Zhang, J. Zhao, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, and Y. Xie, “PRIME: A Novel Processing-in-Memory Architecture for Neural Network Computation in ReRAM-based Main Memory,” ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 27-39, Jun. 2016.
[20] F. Su, W. Chen, L. Xia, C. Lo, T. Tang, Z. Wang, K. Hsu, M. Cheng, J. Li, Y. Xie, Y. Wang, M. Chang, H. Yang, and Y. Liu, “A 462GOPs/J RRAM-Based Nonvolatile Intelligent Processor for Energy Harvesting IoE System Featuring Nonvolatile Logics and Processing-in-Memory,” in Symposium on VLSI Technology, pp. C260-C261, Jun. 2017.
[21] Q. Xia, and J. Yang, “Memristive Crossbar Arrays for Brain-Inspired Computing,” Nature Materials, vol. 18, pp. 309-323, Apr. 2019.
[22] J. Yang, D. Strukov, and D. Stewart, “Memristive Devices for Computing,” Nature Nanotechnology, vol. 8, no. 13, pp. 13-24, Dec. 2012.
[23] M. Prezioso, F. Bayat, B. Hoskins, G. Adam, K. Likharev, and D. Strukov, “Training and Operation of an Integrated Neuromorphic Network Based on Metal-Oxide Memristors,” Nature, vol. 521, pp. 61-64, May 2015.
[24] S. Yu, “Neuro-Inspired Computing With Emerging Nonvolatile Memory,” Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 106, no. 2, pp. 260-285, Feb. 2018.
[25] H. Wu, X. Wang, B. Gao, N. Deng, Z. Lu, B. Haukness, G. Bronner, and H. Qian, “Resistive Random Access Memory for Future Information Processing System,” Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 105, no. 9, pp. 1770–1789, Sep. 2017.
[26] P. Huang, J. Kang, Y. Zhao, S. Chen, R. Han, Z. Zhou, Z. Chen, W. Ma, M. Li, L. Liu, and X. Liu, “Reconfigurable Nonvolatile Logic Operations in Resistance Switching Crossbar Array for Large-Scale Circuits,” Advanced Materials, vol. 28, no. 44, pp. 9758-9764, Nov. 2016.
[27] Y. Zhou, Y. Li, N. Duan, Z. Wang, K. Lu, M. Jin, L. Cheng, S. Hu, T. Chang, H. Sun, K. Xue, and X. Miao, “Boolean and Sequential Logic in a One-Memristor-One-Resistor (1M1R) Structure for In-Memory Computing,” Advanced Electronic Materials, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 1800229(1-9), Jun. 2018.
[28] H. Zhang, W. Kang, K. Cao, B. Wu, Y. Zhang, and W. Zhao, “Spintronic Processing Unit in Spin Transfer Torque Magnetic Random Access Memory,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 2017 – 2022, Apr. 2019.
[29] H. Zhang, W. Kang, L. Wang, K. L. Wang, and W. Zhao, “Stateful Reconfigurable Logic via a Single-Voltage-Gated Spin Hall-Effect Driven Magnetic Tunnel Junction in a Spintronic Memory,” IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 64, no. 10, pp. 4295-4301, Oct. 2017.
[30] W. Kang, H. Wang, Z. Wang,Y. Zhang, and W. Zhao, “In-Memory Processing Paradigm for Bitwise Logic Operations in STT-MRAM,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 1-4, Nov. 2017.
[31] Z. Jiang, S. Yin, J. Seo, and M. Seok, “XNOR-SRAM In-Bitcell Computing SRAM Macro based on Resistive Computing Mechanism,” in Proceedings of the on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, pp. 417-422, May 2019.
[32] H. Valavi, P. Ramadge, E. Nestler, and N. Verma, “A 64-Tile 2.4-Mb In-Memory-Computing CNN Accelerator Employing Charge-Domain Compute,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 54, no. 6, pp. 1789-1799, Jun. 2019.
[33] V. Seshadri, D. Lee, T. Mullins, H. Hassan, A. Boroumand, J. Kim, M. Kozuch, O. Mutlu, P. Gibbons, and T. Mowry, “Ambit: In-Memory Accelerator for Bulk Bitwise Operations Using Commodity Dram Technology,” in Proceedings of the 50th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, pp. 273–287, Oct. 2017.
[34] S. Li, D. Niu, K. Malladi, H. Zheng, B. Brennan, and Y. Xie, “Drisa: A Dram-Based Reconfigurable in-Situ Accelerator,” in Proceedings of the 50th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, pp. 288–301, Oct. 2017.
[35] A. Patil, H. Hua, S. Gonugondla, M. Kang, and N. Shanbhag, “An MRAM-based Deep In-Memory Architecture for Deep Neural Networks,” in IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 1-5, May 2019.
[36] S. Li, C. Xu, Q. Zou, J. Zhao, Y. Lu, and Y. Xie, “Pinatubo: A Processing-in-Memory Architecture for Bulk Bitwise Operations in Emerging Non-Volatile Memories,” in ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), pp. 1-6, Jun. 2016
[37] S. Angizi, Z. He, and D. Fan, “PIMA-Logic: A Novel Processing-in-Memory Architecture for Highly Flexible and Energy-Efficient Logic Computation,” in Proceedings of the 55th Annual Design Automation Conference (DAC), Jun. 2018.
[38] Z. Wang, Y. Su, Y. Li, Y. Zhou, T. Chu, K. Chang, T. Chang, T. Tsai, S. Sze, and X. Miao, “Functional Complete Boolean Logic in 1T1R Resistive Random Access Memory,” IEEE Electron Device Letters, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 179 – 182, Feb. 2017
[39] N. Wald, and S. Kvatinsky, “Design Methodology for Stateful Memristive Logic Gates,” in IEEE International Conference on the Science of Electrical Engineering (ICSEE), pp. 1-5, Nov. 2016.
[40] H. Zhang, W. Kang, B. Wu, P. Ouyang, E. Deng, Y. Zhang, and W. Zhao, “Spintronic Processing Unit Within Voltage-Gated Spin Hall Effect MRAMs,” IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, vol. 18, pp. 473 – 483, May 2019.
*免责声明:本文由作者原创。文章内容系作者个人观点,半导体行业观察转载仅为了传达一种不同的观点,不代表半导体行业观察对该观点赞同或支持,如果有任何异议,欢迎联系半导体行业观察。
今天是《半导体行业观察》为您分享的第2276期内容,欢迎关注。
推荐阅读
★ 芯片“备胎”计划
半导体行业观察

『 半导体第一垂直媒体 』
实时 专业 原创 深度
识别二维码 ,回复下方关键词,阅读更多
存储|射频|CMOS| 设备 |FPGA |晶圆|苹果|海思|半导体股价
回复
投稿
,看《如何成为“半导体行业观察”的一员 》
回复 搜索 ,还能轻松找到其他你感兴趣的文章!
-

- 半导体行业观察
-

- 摩尔芯闻
最新新闻
热门文章 本日 七天 本月
- 1 东方晶源YieldBook 3.0 “BUFF叠满” DMS+YMS+MMS三大系统赋能集成电路良率管理
- 2 NVIDIA重磅出击:三台计算机助力人形机器人飞跃
- 3 奕行智能(EVAS Intelligence)完成数亿元A轮融资,加速推出RISC-V计算芯片产品,共同助力新时代到来
- 4 智能驾驶拐点将至,地平线:向上捅破天,向下扎深根